Overview of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests
Laboratory and diagnostic tests are essential tools in healthcare, providing critical data for disease diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment planning. These tests include blood analyses, imaging studies, and biopsies, aiding in identifying conditions like cancer or metabolic disorders; They serve as a cornerstone in clinical decision-making, ensuring accurate and timely patient care.

1.1 Importance in Medical Diagnosis
Laboratory and diagnostic tests are cornerstone tools in medical diagnosis, enabling healthcare providers to identify diseases, monitor progression, and guide treatment. They provide objective, accurate, and timely information about a patient’s health status. These tests help confirm clinical suspicions, detect abnormalities, and rule out conditions, ensuring precise diagnoses. By analyzing blood, tissue, and other specimens, they reveal vital insights into metabolic, infectious, and chronic diseases. Early detection through diagnostic tests improves patient outcomes, prevents complications, and enhances the effectiveness of interventions. Their role is indispensable in modern medicine, forming the basis for evidence-based decision-making and personalized care plans.
1.2 Scope and Applications
Laboratory and diagnostic tests encompass a wide range of applications, from diagnosing diseases to monitoring treatment efficacy. They are used to detect abnormalities, assess organ function, and identify infectious agents. These tests are integral in preventive care, enabling early detection of conditions like cancer and metabolic disorders. Their scope extends across various medical specialties, including oncology, cardiology, and infectious diseases. Advanced tests, such as biopsies and imaging studies, provide detailed insights into tissue and organ health. By analyzing blood, urine, and other specimens, these tests help guide personalized treatment plans, ensuring accurate and effective patient care across diverse clinical scenarios.

Types of Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests include blood tests, imaging studies, and tissue biopsies. These diagnostics help identify diseases, monitor health, and guide treatment decisions accurately and effectively.
2.1 Blood Tests
Blood tests are a fundamental diagnostic tool, measuring various components like red and white blood cells, hemoglobin, and ferritin. They help assess anemia, infection, and organ function, providing crucial insights for accurate diagnoses and treatment plans. Regular monitoring ensures timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.
2.2 Imaging and Radiologic Tests
Imaging and radiologic tests are crucial for visualizing internal body structures, aiding in the detection of abnormalities such as tumors, fractures, or organ enlargement. Techniques include X-rays, CT scans, MRI, and ultrasounds, each providing detailed insights into specific conditions. These non-invasive or minimally invasive procedures guide accurate diagnoses and treatment plans, enhancing patient care and outcomes.

Patient Preparation and Specimen Collection
Patient preparation involves following specific instructions, such as fasting or avoiding medications, to ensure accurate test results. Proper specimen collection and handling are critical for reliable diagnostic outcomes.
3.1 Pre-Test Requirements
Pre-test requirements ensure accurate and reliable results. Patients may need to fast, avoid certain medications, or prepare physically. Clear communication of instructions is vital to minimize errors and complications during specimen collection.
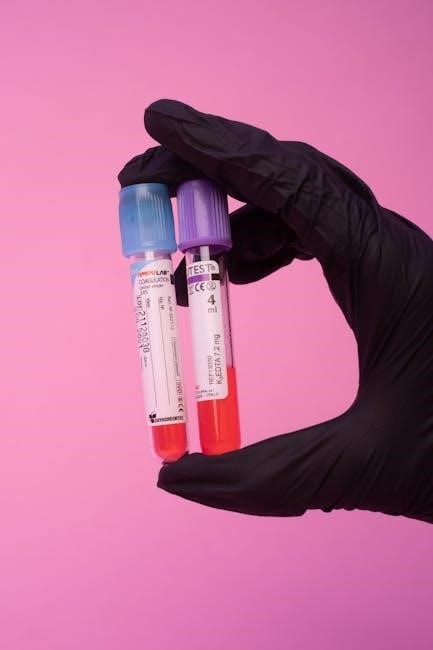
3.2 Proper Specimen Handling
Proper specimen handling is critical for accurate test results and patient safety. This includes using appropriate containers, labels, and storage conditions to preserve sample integrity. Protective gear like gloves and lab coats must be worn to prevent exposure to biohazards. Specimens should be transported promptly to the laboratory in sealed, leak-proof containers to avoid contamination. Correct labeling ensures samples are matched to the right patient, reducing mix-ups. Improper handling can lead to inaccurate results, delays, or potential health risks. Adhering to established protocols ensures reliability and safety throughout the diagnostic process.
Understanding Test Results
Understanding test results involves interpreting numerical values, abnormal findings, and reference ranges to diagnose conditions accurately. Healthcare providers use these results to guide treatment decisions and monitor progress.
4.1 Interpreting Results
Interpreting laboratory results involves comparing test values to reference ranges, considering patient-specific factors like age and health status. Abnormal levels may indicate underlying conditions, guiding further investigation or treatment. Healthcare providers analyze results in context, ensuring accurate diagnoses and personalized care plans. Proper interpretation also involves recognizing patterns and correlations between multiple tests, enhancing diagnostic accuracy and clinical decision-making. Clear communication of results to patients and other healthcare professionals is essential for effective care.
4.2 Reference Ranges and Normal Values
Reference ranges, also known as normal values, are standardized intervals used to interpret laboratory test results. These ranges are established based on data from healthy individuals, accounting for variations due to age, sex, and other factors. A result within the reference range suggests normal physiological function, while values outside may indicate a potential health issue. These ranges are crucial for accurate diagnosis and monitoring, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions. Reference values may vary slightly between laboratories due to differences in testing methods, emphasizing the importance of using the same lab for serial measurements to ensure consistency and reliability.

Laboratory Safety and Biohazard Handling
Laboratory safety involves strict protocols to protect personnel from biohazards. Proper PPE, safe specimen handling, and disposal are critical to minimizing risks and ensuring a secure environment.
5.1 Safety Protocols
Safety protocols in laboratories are designed to protect personnel from biohazards and chemical risks. Key measures include wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), proper handling of specimens, and safe chemical storage. Regular training ensures compliance with regulations, minimizing exposure risks and maintaining a secure working environment. Adherence to these protocols is critical for preventing accidents and ensuring the well-being of laboratory staff.

Application in Clinical Practice
Laboratory and diagnostic tests play a crucial role in clinical practice, aiding in disease diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring. They guide personalized patient care and improve health outcomes significantly.
6.1 Role in Diagnostics and Treatment
Laboratory and diagnostic tests are pivotal in identifying diseases, assessing their severity, and guiding treatment plans. They enable healthcare providers to confirm diagnoses, monitor therapeutic responses, and adjust interventions. By providing accurate and timely data, these tests facilitate personalized care, enhancing patient outcomes and optimizing resource utilization. Regular monitoring through such tests ensures that treatments remain effective and minimizes potential complications, playing a central role in modern clinical practice.
Advances and Future Trends
Emerging technologies, such as AI and point-of-care testing, are transforming laboratory diagnostics. These innovations enhance accuracy, speed, and accessibility, paving the way for personalized medicine and improved patient outcomes.
7.1 Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies in laboratory diagnostics include artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, which enhance test accuracy and speed. Point-of-care testing devices enable rapid, decentralized diagnostics, improving accessibility. Advances in genomics and proteomics allow for personalized medicine, tailoring treatments to individual profiles. Additionally, wearable health monitors and telemedicine platforms integrate with lab systems, offering real-time data and remote patient monitoring. These innovations are revolutionizing healthcare, making diagnostics more efficient, precise, and patient-centric, while reducing costs and improving overall outcomes. The future of lab testing lies in seamless integration of technology and healthcare, driving advancements that benefit both clinicians and patients alike.